Daphniphyllum Macropodum: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Characteristics and Uses
Overview of Daphniphyllum Macropodum
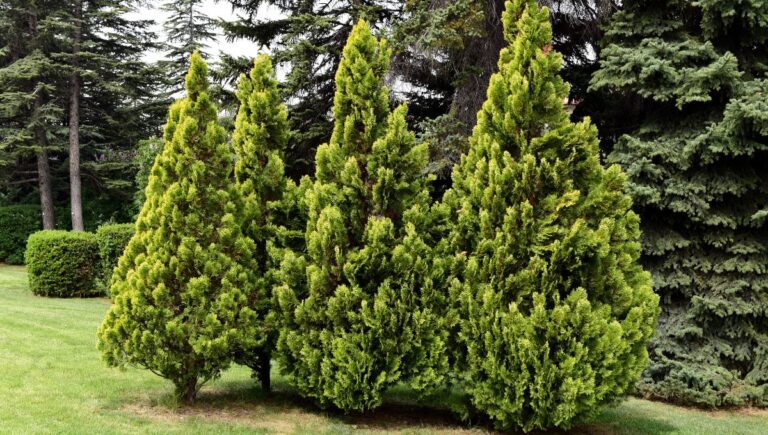
Daphniphyllum macropodum is an evergreen shrub or small tree that belongs to the Daphniphyllaceae family. It is native to China, Japan, and Korea. This plant is known for its medicinal properties and has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries.
The genus Daphniphyllum contains around 120 species of evergreen shrubs and small trees. Daphniphyllum macropodum is one of the most well-known species in this genus. The plant can grow up to 10 meters tall and has glossy, dark green leaves.
The leaves of Daphniphyllum macropodum contain various alkaloids, which have been found to have antiviral, antibacterial, and antitumor properties. These alkaloids have been used to treat a variety of ailments, including influenza, hepatitis, and cancer.
Daphniphyllum macropodum is also known for its insecticidal properties. Several alkaloids isolated from the bark of the plant have been found to be effective against a variety of insects, including the mosquito that carries the Zika virus.
In addition to its medicinal properties, Daphniphyllum macropodum is also valued for its ornamental qualities. The plant has attractive foliage and produces small, inconspicuous flowers that are followed by red or black berries.
Overall, Daphniphyllum macropodum is a versatile plant that has been used for medicinal, insecticidal, and ornamental purposes. Its alkaloids have been found to have a wide range of properties, making it a valuable resource for researchers and traditional healers alike.
Taxonomy and Classification
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a species of flowering plant in the family Daphniphyllaceae. It was first described by Blume in 1850 as Daphniphyllum humile subsp. macropodum, but later elevated to species status. The genus Daphniphyllum contains around 50 species of evergreen shrubs and trees, distributed mainly in Asia.
Taxonomically, Daphniphyllum macropodum has been classified in different ways over the years. In the past, some authors have included it in the genus Wikstroemia, while others have placed it in the family Thymelaeaceae. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have confirmed its placement in the family Daphniphyllaceae.
Within the genus Daphniphyllum, Daphniphyllum macropodum is classified in the section Daphniphyllum, which includes around 20 species. This section is characterized by the presence of unisexual flowers, with the male and female flowers borne on separate plants.
The classification of Daphniphyllum species is based on a combination of morphological, anatomical, and molecular characters. Some of the morphological characters used to distinguish between species include leaf shape, venation, and arrangement, flower size and shape, and fruit morphology.
Overall, the taxonomic and classification status of Daphniphyllum macropodum is well-established, and it is recognized as a distinct species within the genus Daphniphyllum.
Geographical Distribution
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a species of flowering plant that is native to China, Korea, and Japan. It is commonly found in the broad-leaved evergreen forests of these regions. The plant is also known as the Himalayan daphne, due to its presence in the Himalayan mountain range.
In the United States, Daphniphyllum macropodum is found in a few states, including California, Colorado, Hawaii, Oregon, Idaho, Utah, Florida, Alaska, and Washington. However, it is not native to these regions and is instead grown as an ornamental plant.
The plant prefers to grow in areas with partial shade and moist, well-drained soil. It can tolerate a range of temperatures, from cold winters to hot summers. In its native regions, Daphniphyllum macropodum can be found at elevations ranging from sea level to over 2,000 meters.
Overall, Daphniphyllum macropodum has a wide geographical distribution, spanning across multiple countries and regions. Its ability to grow in a variety of conditions has contributed to its popularity as an ornamental plant in many parts of the world.
Physical Characteristics
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a tree that can grow up to 15 meters in height. The stem is typically oblong and can range in color from blue-black to dark green. The leaves of Daphniphyllum macropodum are glaucous, which means they have a powdery or waxy coating that gives them a bluish-green appearance. The foliage is rhododendron-like and can be pale green, reddish, or tinged with red.
The leaves of Daphniphyllum macropodum are alternate and have a petiole that is about 1-2 cm long. The stalk of the leaf is about 1-2 cm long as well. The leaves are typically elliptical or ovate in shape and can reach up to 20 cm in length and 12 cm in width. The leaf margins are entire, which means they are smooth and not serrated.
The flowers of Daphniphyllum macropodum are small, inconspicuous, and greenish-yellow in color. The fruits are drupes that are about 1 cm in diameter and contain a single seed. The drupes are initially green but turn black when they mature.
Overall, the physical characteristics of Daphniphyllum macropodum are unique and distinctive. The foliage, in particular, is notable for its rhododendron-like appearance and glaucous coating. If you are looking for a tree with striking physical characteristics, Daphniphyllum macropodum is definitely worth considering.
Floral Traits
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a dioecious plant, meaning that male and female flowers are produced on separate plants. The flowers of Daphniphyllum macropodum are small and inconspicuous, with creamy white petals that are often tinged with purple-pink.
The flowers are arranged in racemes, which are clusters of flowers that grow along a central stem. Each flower typically has five petals and five stamens, which are the male reproductive organs. The female flowers have a single pistil, which is the female reproductive organ.
The flowers of Daphniphyllum macropodum are surrounded by bracts, which are modified leaves that are often mistaken for petals. These bracts are typically green and may be tinged with purple-pink, depending on the variety.
Daphniphyllum macropodum typically blooms in the spring, from March to May. The flowers are not particularly showy, but they are an important part of the plant’s reproductive cycle.
In summary, the flowers of Daphniphyllum macropodum are small and inconspicuous, with creamy white petals that are often tinged with purple-pink. They are arranged in racemes and surrounded by bracts. The plant is dioecious, with male and female flowers produced on separate plants. The flowers are an important part of the plant’s reproductive cycle and typically bloom in the spring.
Cultivation and Care
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a beautiful evergreen shrub or small tree that is native to China, Japan, and Korea. It is a hardy plant that can grow up to 20 feet tall and wide. Here are some tips on how to cultivate and care for this plant.
Soil and pH
Daphniphyllum macropodum prefers moist, well-drained soil that is slightly acidic to neutral. The pH level should be between 5.0 and 7.0. If your soil is too alkaline, you can add sulfur to lower the pH level.
Sunlight
Daphniphyllum macropodum prefers partial shade to semi-shade. It can tolerate full sun, but it may need winter protection in colder climates.
Hardy and USDA Zone
Daphniphyllum macropodum is hardy in USDA zones 7 to 9. In colder climates, it may need winter protection.
Water and Moisture
Daphniphyllum macropodum prefers moist, well-drained soil. Water the plant deeply once a week during the growing season. Reduce watering in the winter.
New Growth
Daphniphyllum macropodum produces new growth in the spring. Prune the plant after it has finished blooming to promote new growth.
In summary, Daphniphyllum macropodum is a hardy plant that requires moist, well-drained soil, partial shade to semi-shade, and deep watering during the growing season. With proper care, it can be a beautiful addition to your garden.
Propagation Techniques
If you are interested in propagating Daphniphyllum macropodum, there are a few techniques that can be used. The most common propagation technique is through stem cuttings. Stem cuttings should be taken in the early summer when the plant is actively growing. Cuttings should be taken from the current year’s growth and should be about 6 inches long. Remove the leaves from the lower half of the cutting and dip the cut end in rooting hormone. Place the cutting in a pot filled with a well-draining soil mix and keep it moist. The cutting should root in about 4-6 weeks.
Another propagation technique that can be used is root cuttings. While not as commonly used as stem cuttings, root cuttings can be successful in propagating Daphniphyllum macropodum. Root cuttings should be taken in the late winter or early spring when the plant is dormant. Cut the roots into sections that are about 2-3 inches long and plant them in a pot filled with a well-draining soil mix. Keep the soil moist and the cutting should root in about 4-6 weeks.
Propagation from seed is also possible, but it can be more challenging than other techniques. Seeds should be collected in the fall and stratified over the winter. Stratification involves placing the seeds in a moist medium and keeping them in a cool location for several months. Once stratified, the seeds can be planted in a well-draining soil mix and kept moist. Germination can take several months to a year.
Overall, stem cuttings are the most common and reliable propagation technique for Daphniphyllum macropodum. However, root cuttings and seed propagation can also be successful with proper care and attention.
Significance and Uses
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a versatile plant that has many uses and benefits. In this section, we will discuss some of the most significant uses of this plant.
Ornamental
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a popular ornamental plant due to its attractive foliage and unique appearance. Its glossy, dark green leaves and red berries make it an excellent specimen for landscaping and garden design. It is also a popular choice for bonsai enthusiasts due to its small size and adaptability.
Construction
Daphniphyllum macropodum wood is strong, durable, and resistant to decay, making it an ideal material for construction and furniture making. Its wood is also used for carving and decorative purposes due to its unique grain patterns and coloration.
Medicinal
Daphniphyllum macropodum leaves and bark contain alkaloids and other compounds that have been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. They are believed to have anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anticancer properties and are used to treat a variety of ailments such as rheumatism, fever, and coughs.
Other Uses
Daphniphyllum macropodum is also used in the production of insecticides and as a natural dye for textiles. Its leaves and berries are also used as a food source for wildlife such as birds and small mammals.
Overall, Daphniphyllum macropodum is a versatile plant with many uses and benefits. Whether you are looking for an attractive ornamental plant, a durable material for construction, or a natural remedy for various ailments, Daphniphyllum macropodum has something to offer.
Potential Challenges
While Daphniphyllum macropodum has many potential benefits, there are also some challenges associated with the plant. Here are some of the potential challenges you may face if you decide to grow or use Daphniphyllum macropodum:
Frost Sensitivity
Daphniphyllum macropodum is sensitive to frost, which can damage or kill the plant. If you live in an area with cold winters, you may need to take extra precautions to protect your plants. This could include covering them with frost blankets or moving them indoors during the winter months.
Male Pollinator Required
Daphniphyllum macropodum is dioecious, meaning that male and female flowers are borne on separate plants. This means that if you want your female plants to produce fruit, you will need to have at least one male plant nearby to provide pollen. If you only have female plants, you will not get any fruit.
Other Challenges
In addition to frost sensitivity and the need for a male pollinator, there may be other challenges associated with growing or using Daphniphyllum macropodum. For example, the plant may be difficult to propagate from cuttings, and it may be susceptible to certain pests or diseases. It is important to do your research and understand the potential challenges before you decide to grow or use this plant.
Overall, while there are some potential challenges associated with Daphniphyllum macropodum, many people find that the benefits of this plant outweigh the drawbacks. By taking the time to understand the potential challenges and how to address them, you can ensure that your experience with Daphniphyllum macropodum is a positive one.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where can I buy Daphniphyllum macropodum?
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a popular ornamental plant that can be found in many nurseries and garden centers. You can also purchase it online from various plant retailers. Make sure to buy from a reputable seller and check the plant’s growing requirements before purchasing.
How tall does Daphniphyllum macropodum grow?
Daphniphyllum macropodum can grow up to 15 meters tall in the wild, but it typically grows to about 3-5 meters in cultivation. The plant has a slow growth rate and may take several years to reach its full height.
Is Daphniphyllum macropodum variegated?
No, Daphniphyllum macropodum is not typically variegated. Its leaves are dark green and glossy, with a leathery texture. However, there are other species of Daphniphyllum that have variegated leaves.
What is Daphniphyllum himalayense?
Daphniphyllum himalayense is a species of Daphniphyllum that is native to the Himalayas. It has similar growing requirements to Daphniphyllum macropodum and is also grown as an ornamental plant.
What is the common name for Daphniphyllum macropodum?
Daphniphyllum macropodum is commonly known as the Himalayan Daphne or the Longpod Daphne.
What is the habitat of Daphniphyllum macropodum?
Daphniphyllum macropodum is native to the Himalayan region and can be found growing in forests and mountainous areas. It prefers well-drained soil and partial shade, and can tolerate cold temperatures. In cultivation, it is often grown as an understory plant or in shaded areas.
Daphniphyllum macropodum is a popular ornamental plant that can be found in many nurseries and garden centers. You can also purchase it online from various plant retailers. Make sure to buy from a reputable seller and check the plant’s growing requirements before purchasing.
“}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”How tall does Daphniphyllum macropodum grow?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Daphniphyllum macropodum can grow up to 15 meters tall in the wild, but it typically grows to about 3-5 meters in cultivation. The plant has a slow growth rate and may take several years to reach its full height.
“}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”Is Daphniphyllum macropodum variegated?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
No, Daphniphyllum macropodum is not typically variegated. Its leaves are dark green and glossy, with a leathery texture. However, there are other species of Daphniphyllum that have variegated leaves.
“}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is Daphniphyllum himalayense?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Daphniphyllum himalayense is a species of Daphniphyllum that is native to the Himalayas. It has similar growing requirements to Daphniphyllum macropodum and is also grown as an ornamental plant.
“}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is the common name for Daphniphyllum macropodum?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Daphniphyllum macropodum is commonly known as the Himalayan Daphne or the Longpod Daphne.
“}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is the habitat of Daphniphyllum macropodum?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Daphniphyllum macropodum is native to the Himalayan region and can be found growing in forests and mountainous areas. It prefers well-drained soil and partial shade, and can tolerate cold temperatures. In cultivation, it is often grown as an understory plant or in shaded areas.
“}}]}